But a new report shows there were a lot more victims than in previous years
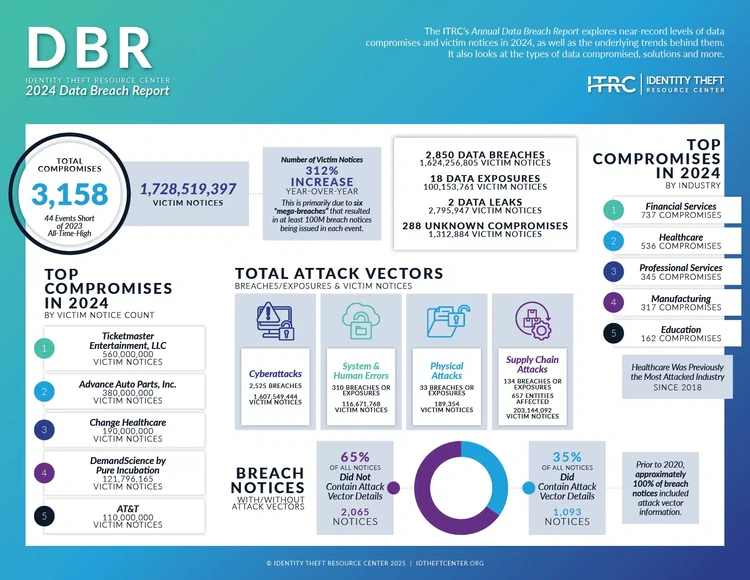
In 2024, the landscape of data breaches remained largely unchanged in terms of the number of incidents, with 3,158 compromises reported, mirroring the previous year's figures. However, the year was marked by significant shifts in the nature and impact of these breaches, according to a report by the Identity Theft Resource Center.
One of the most striking trends was the dramatic 312% increase in victim notices, totaling over 1.7 billion. This surge was primarily driven by six "mega-breaches," each resulting in at least 100 million notices, collectively accounting for more than 1.4 billion of the total notices issued. These mega-breaches underscored the growing scale and impact of cybersecurity incidents on individuals and organizations alike.
Despite the overall stability in the number of breaches, there was a 58% decline in compromises linked to system and human errors. Physical attack-related breaches, such as those involving skimmers and stolen devices, also reached a six-year low, with only 33 incidents reported.
Publicly traded companies, although representing a mere 7% of all compromised organizations, were responsible for issuing a staggering 76% of victim notices. This disproportionate figure highlights the significant impact of breaches within these entities.
Among the 133 cyberattacks against publicly traded companies, stolen credentials emerged as the leading attack vector. However, a concerning 74% of these organizations did not specify the attack vector in their breach notices, reflecting a growing trend of non-disclosure.
Banks were prime targets
The Financial Services sector, led by commercial banks and insurance companies, emerged as the most breached industry in 2024, overtaking Healthcare, which had held this position since 2018. Other affected sectors included professional services, manufacturing, and technology.
Cyberattacks continued to be the primary cause of data breaches. Yet, the specificity of attack vectors in breach notices has been on a decline for five consecutive years. In 2024, approximately 70% of cyberattack-related notices lacked detailed attack information, a significant increase from 58% in 2023. This trend contrasts sharply with 2019 and earlier years, when nearly all breach notices included such details.
Excluding the mega-breaches, the remaining victim notices amounted to approximately 266 million, representing a 36% decrease compared to the previous year. This decline suggests improvements in certain areas of cybersecurity, although the overall impact of mega-breaches continues to overshadow these gains.
As the digital landscape evolves, the need for robust cybersecurity measures and transparent reporting becomes increasingly critical to safeguard against the growing threat of data breaches.
Photo Credit: Consumer Affairs News Department Images
Posted: 2025-01-29 19:29:49